What is the
Integrated Methane Inversion?
The
Integrated Methane Inversion (IMI)
is a user-friendly research-grade cloud-computing tool for
estimating total methane emissions for any domain and period of
interest
by analytical inversion of satellite observations from the TROPOspheric
Monitoring Instrument (TROPOMI). It enables researchers and stakeholders
to
infer methane emissions at up to 0.25° × 0.3125° (≈ 25 × 25 km²)
spatial resolution
and up to weekly temporal resolution from
TROPOMI satellite data resident on the Amazon Web Services (AWS)
cloud, without requiring expert knowledge of inverse methods or cumbersome
data download.
The IMI uses the
GEOS-Chem 3-D chemical transport model
driven by NASA Goddard Earth Observing System (GEOS) meteorological data
as a forward model for the inversion. It uses
cutting-edge algorithms developed by the Harvard Atmospheric
Chemistry Modeling Group (ACMG)
in collaboration with the Netherlands Institute for Space Research
(SRON) and documented extensively in the peer-reviewed research
literature.
It is strongly documented and fully open-code to ensure transparency,
reproducibility, and integrity of the results.
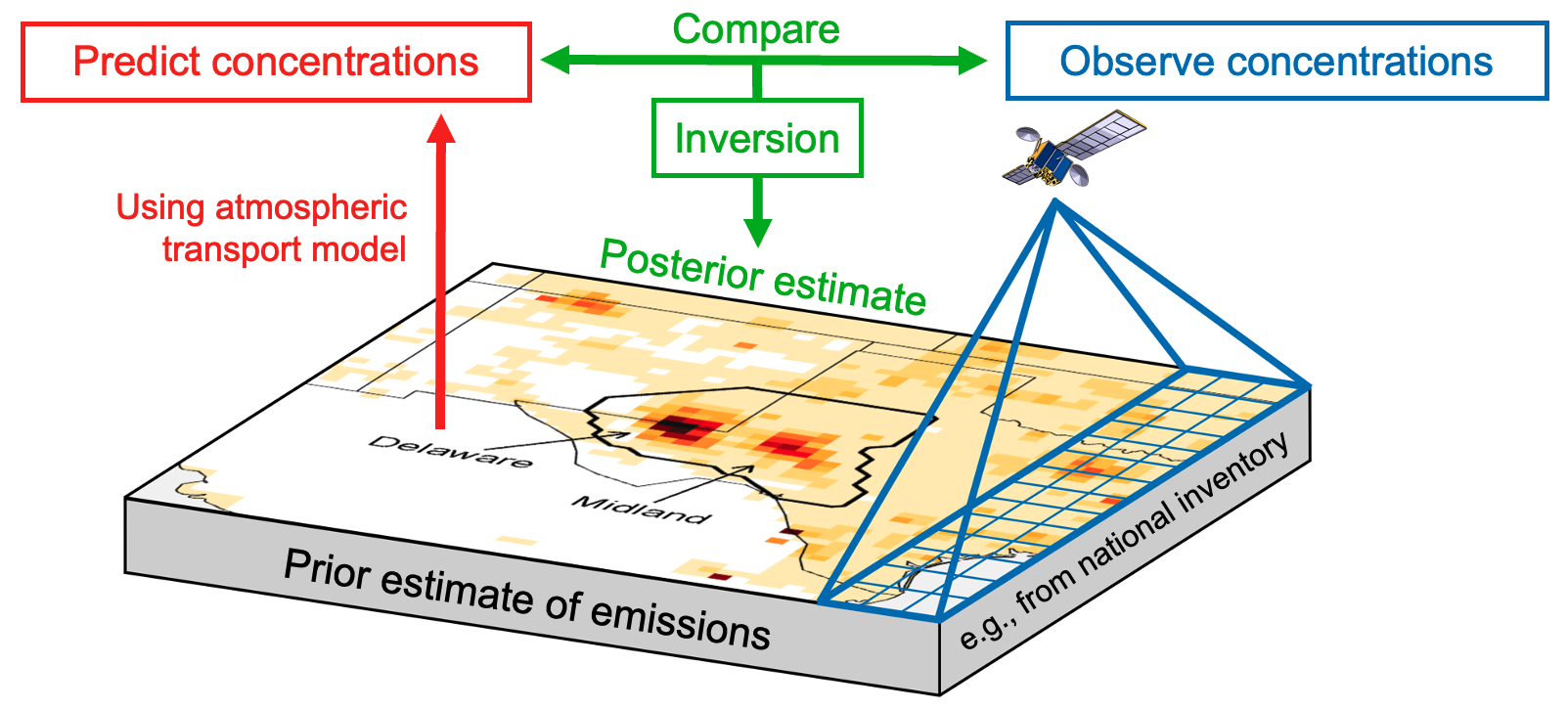
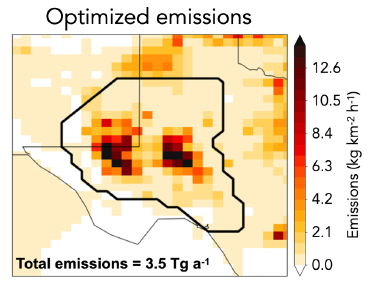
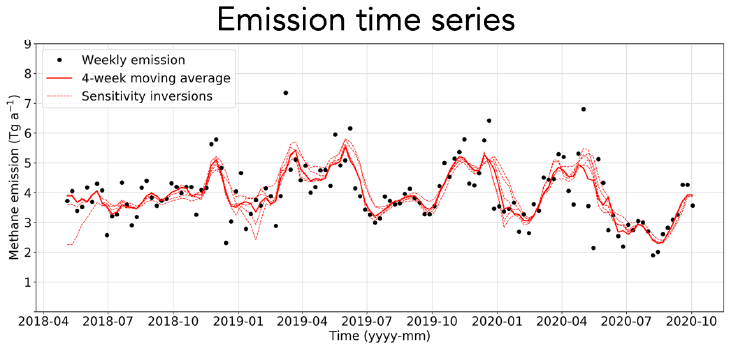
An IMI preview feature allows the users to display the
satellite observations for their domain and period of interest along
with prior emission inventories, point source data, and expected
information to be achieved from the inversion.
Integral Earth, a new simple web interface under development, will allow non-experts to access the IMI with no learning curve. Leave it to the experts at Harvard to set up and conduct your inversion, and receive complete results with full transparency of methods used.
How do I Access the IMI?
The IMI is an open-source software project and freely accessible via the AWS Marketplace.To get started with the IMI, read the documentation on the IMI readthedocs site. Instructions are provided to configure the IMI, run it on AWS, and visualize output.
- To view the IMI source code, visit our GitHub repo.
- For a high-level scientific description, see the IMI development papers by Varon et al. (2022) and Estrada et al. (2024).
We encourage new users to email us at
integrated-methane-inversion@g.harvard.edu
with a description of your project. This helps us identify priorities for
new features and updates.
User technical support can also be provided via this email.
Users can also submit issues via our
Github repo
to contribute to development.
Collaboration
The IMI is a contribution to the NASA Carbon Monitoring System and a collaboration between the Harvard Atmospheric Chemistry Modeling Group (ACMG) and the Netherlands Institute for Space Research (SRON). ACMG development of the IMI is supported in part by ExxonMobil. Please let us know if you are interested in supporting the IMI.